What Does Meningitis Look Like?

Warning

Fungal Meningitis

Parasitic Meningitis

Viral Meningitis

Non-Infectious Meningitis

Bacterial Meningitis



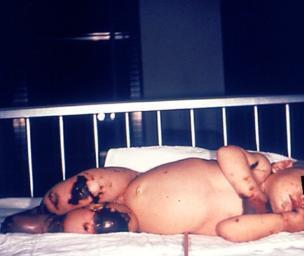








What Is Meningitis?
Meningitis is considered to be an inflammation or swelling of the protective membranes that cover the brain as well as the spinal cord, which is known as the meninges. Bacteria and viruses are mostly known to be the cause of meningitis. However, allergies to certain drugs, chemical irritation, and physical injury are also known to cause meningitis. There are essentially five types of meningitis, and each of them are classified by the cause of the disease. Those five types are: fungal, bacterial, viral, parasitic, and non-infectious. The symptoms for each of these forms are very similar, but with certain differences. Also, the severity as well as the treatment of the disease would differ based on the cause of the medical condition, hence, it is important to identify exactly which type of meningitis the person is suffering from and then look to plan the correct treatment strategy.
- Bacterial meningitis: This is known to be a potentially fatal form of meningitis which can lead to serious complications. Those complications would include damage to the brain, loss of hearing, and, if no proper treatment is given, it can also result in death or coma for the individual. This type of meningitis is known to mostly occur when the bacteria finds its way into the bloodstream of the individual and then travels to the brain and the spinal cord. Some of those bacteria which can lead to bacterial meningitis are streptococcus pneumonia, haemophilus influenza, and Neisseria meningitides. In this case, the bacteria have a tendency to spread from one individual to another through sneezing, the transfer of saliva while kissing or mouth to mouth resuscitation, and, lastly, through coughing. A few types of bacterial meningitis can also be caused when one consumes contaminated food items, even when the source is not known. Some of the sudden symptoms that appear are fever, stiffness in the neck, and headache. Apart from these common symptoms, others include vomiting, rashes, nausea, having a sensitivity towards light, and feelings of confusion. These tend to appear mostly three to seven days once the individual is exposed to the germs that cause the disease. In many cases, the symptoms of bacterial meningitis can be confused with flu symptoms, therefore making a diagnosis difficult. With the help of antibiotics, one can treat bacterial meningitis, so it becomes important to seek treatment at the earliest.
- Fungal meningitis: One of the rare forms of meningitis is the fungal form. It is known to occur when a fungus enters the bloodstream of the individual. Any individual can get this form of meningitis, but those who have an impaired immune system or are already unwell are at an increased risk of getting this type of meningitis. This type is mostly caused due to inhaling fungal spores from contaminated bat droppings, bird droppings, and oil. The treatment would mostly consist of a long course of antifungal drops, which are given in high doses, and mostly they are administered in the hospital through an IV.
- Parasitic meningitis: There is a parasite known as the Naegleria fowleri, which is said to be the primary source for PAM, or primary amebic meningoencephalitis. It is quite a rare form of parasitic meningitis. This type of meningitis leads to a brain infection, which tends to progress rapidly in one to 12 days on average. The standard meningitis symptoms would start to appear in just one to seven days after the infection, which would then be followed by a loss of coordination or balance, hallucinations, seizure attacks, feelings of confusion, and a lack of attention to the surrounding environment. This organism is known to enter the body through the nose, and then it travels to the brain, wherein it starts to destroy the brain tissues. This is not a contagious disease.
- Viral meningitis: This is quite a common type of meningitis and is mostly less severe. Most of the cases seen for viral meningitis are known to be caused due to enteroviruses, but there are other forms of common virus as well, such as measles, chicken pox, and mumps, which spread through mosquito or any other form of insects and have a tendency to lead to viral meningitis. It has symptoms similar to those of bacterial meningitis, including headache, stiffness in the neck, and a sudden fever, but in that, it is aseptic, wherein the bacteria would not grow into the cerebrospinal fluid. It is mostly known to resolve on its own without need for any specific type of medication or treatment, however, one can get it treated with certain antiviral medications. In certain cases, it has a tendency to become fatal based on factors such as which type of virus it is, what caused the infection, the age of the patient, and, lastly, whether or not the individual has a weakened immune system. Viral meningitis is known to spread through fecal contamination, especially when proper handwashing practices are not followed after a visit to the toilet or changing diapers. The enterovirus is also known to spread through the eye, mouth secretions, and the nose. Hence, to prevent such cases, be sure to follow proper good hygiene practices such as hand washing, and be sure that you are vaccinated against mumps, chicken pox, and rubella.
- Non-infectious meningitis: Similar to the fungal and parasitic meningitis forms, non-infectious meningitis is not contagious. It is known to mostly occur as a result of cancer, surgery for the brain, lupus, certain types of medications, and head injuries. The symptoms would be the same as the general form of meningitis, including sudden fever, stiffness in the neck, and headache. The less common symptoms are nausea, altered state of mind, vomiting, and sensitivity towards light.
Symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms in terms of meningitis are recognizable, and it is quite common in most of the types of meningitis. They include:
- Headache
- Stiffness of the neck
- Sudden onset of fever
- Rashes or purple areas on the skin, which may look like bruises
The symptoms are known to mostly appear all of a sudden, just within a weeks’ time of being exposed to the cause of the disease.
A few of the less common symptoms of meningitis include:
- Nausea
- Feelings of confusion, mostly seen in elderly patients
- Vomiting
- Seizure attacks or convulsions
- Sensitivity towards light
- Severe pain in the muscles
- Difficulty waking up
- Rashes, which mostly appear in the later stage of the disease
- Fatigue
- Feeling drowsy all the time
- Skin that turns pale and blotchy
- Coma
In the case of small children, they would tend to display more varied symptoms of meningitis than adults. Stiffness in the neck can be seen as a symptom in adults, but not in children. The symptoms in children would progress very gradually. A few of the symptoms commonly seen in young children are:
Partial attacks of seizures, crying that is mostly high-pitched, getting irritated rather easily, finding it difficult to feed the child, projectile vomiting, and rashes on the skin that are purple or red in color.